Follow best practices with AWS Config and Security Hub
31 May 2023
Configuring the cloud environment is not an easy task. Despite a lot of effort being taken away from ops engineers, it still takes a lot to ensure that our systems are configured correctly, and more important, securely. Today, let me introduce you to AWS Config and AWS Security Hub.
What is AWS Config?
AWS Config is a service that allows you to track changes to your AWS resources and apply rules that will filter our configurations that are not in line with your policies. It's not a tool to enforce policies, but rather to track which ones are broken.
Security Hub is an extension to AWS Config that contains predefined best practices in terms of security. It has a separate dashboard but uses Config under the hood. However, it can also receive findings from other services such as AWS GuardDuty or Macie. It can also emit CloudWatch Events that can be chained further with for example Lambda to automatically fix the issue.
A badly configured environment
I will create some new AWS resources that are not configured correctly. Let's start by adding access keys to the root user. It's one of the worst practices as root user should only be used for emergencies so CLI access shouldn't be needed.
Next, I will create an EC2 instance with security group that allows SSH and MySQL traffic from anywhere. You should restrict who can access your SSH and database ports.
I will also create a MariaDB RDS instance with allowed public access and the same security groups that allow anyone to connect.
Activating AWS Config and Security Hub
In order to check our account for compliance, we need to activate AWS Config and
one or more of the Security Hub standards. First, let's search for Config in
the search bar and activate using 1-Click button. Config is bound to AWS
region.
Next, we need to activate Security Hub. We can do it by searching for
Security Hub. In this example I will use CIS Foundations Benchmark 1.2.
Security Hub is also bound to AWS region.
Checking for compliance
Both dashboards show what rules and resources are compliant and which are not.
However, Security Hub might take up to 24 hours to show the score. However, it
might already show something in Findings tab. By searching for CRITICAL
severity, it seems that the fact that root has access keys is already visible.
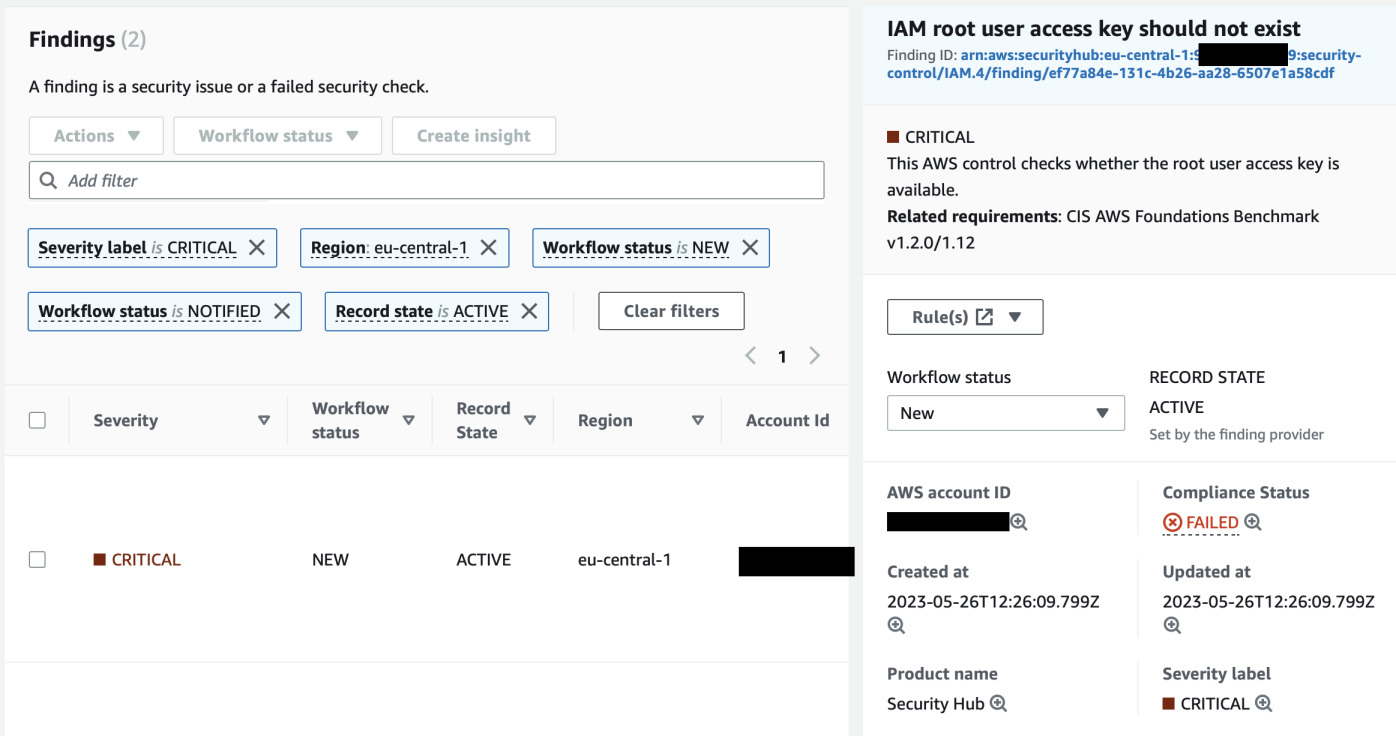
Let's delete the access key and see if it will be marked as compliant. We can follow the rule from Security Hub to be shown in AWS Config. From there we can see how often it is evaluated. For root access keys it is 12 hours. However, there's an option to trigger it manually.
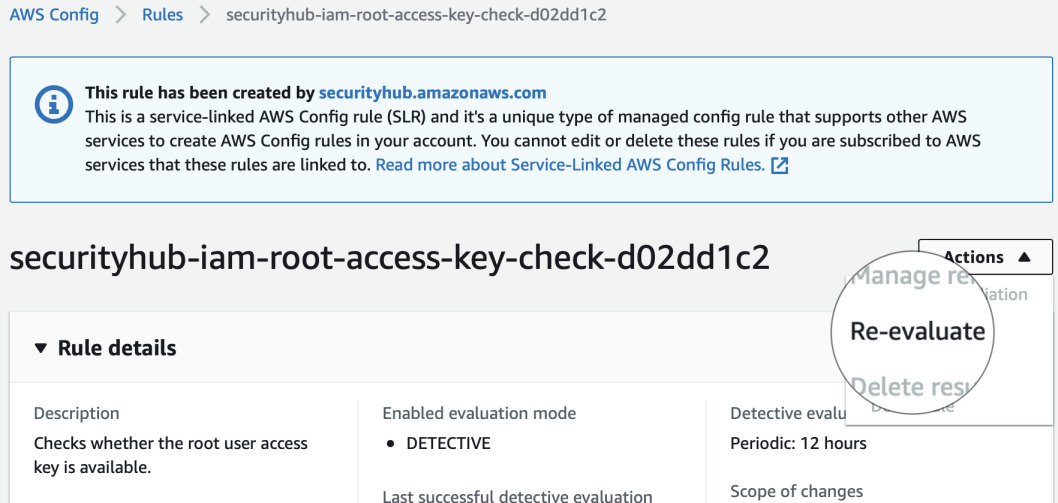
Let's go back to Security Hub and see if it's compliant now. In
Security standards search for IAM.4. It still shows No Data. But let's
click inside the rule.
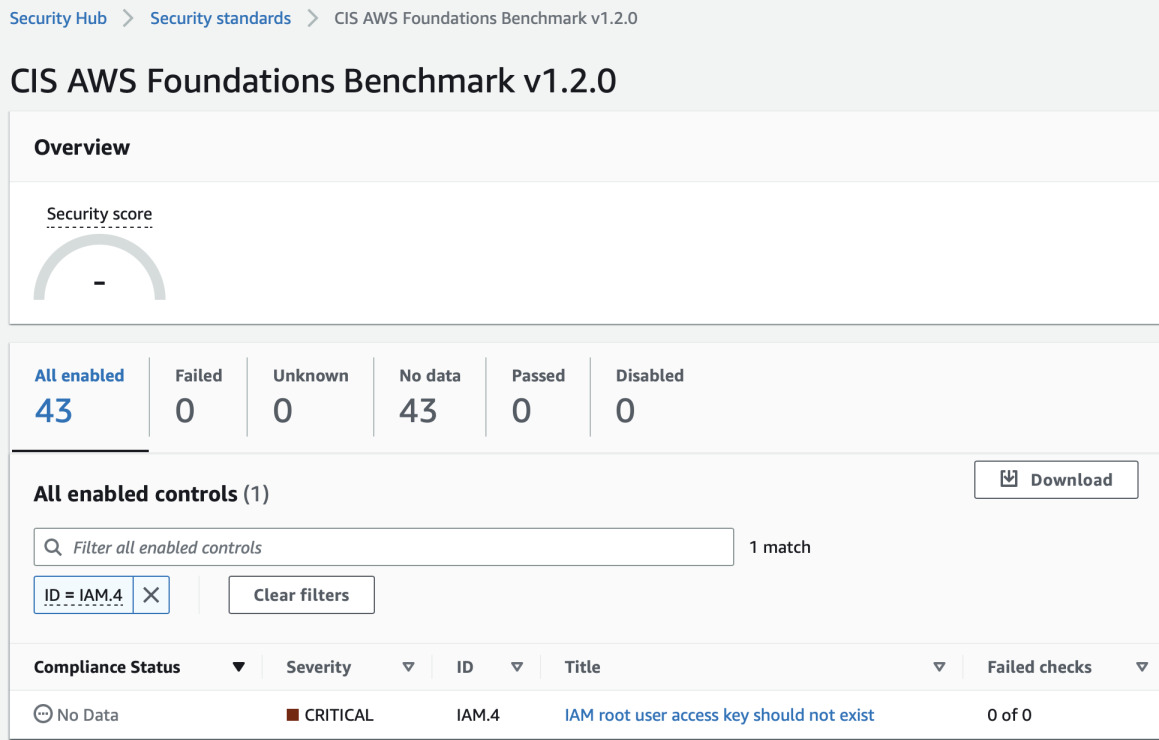
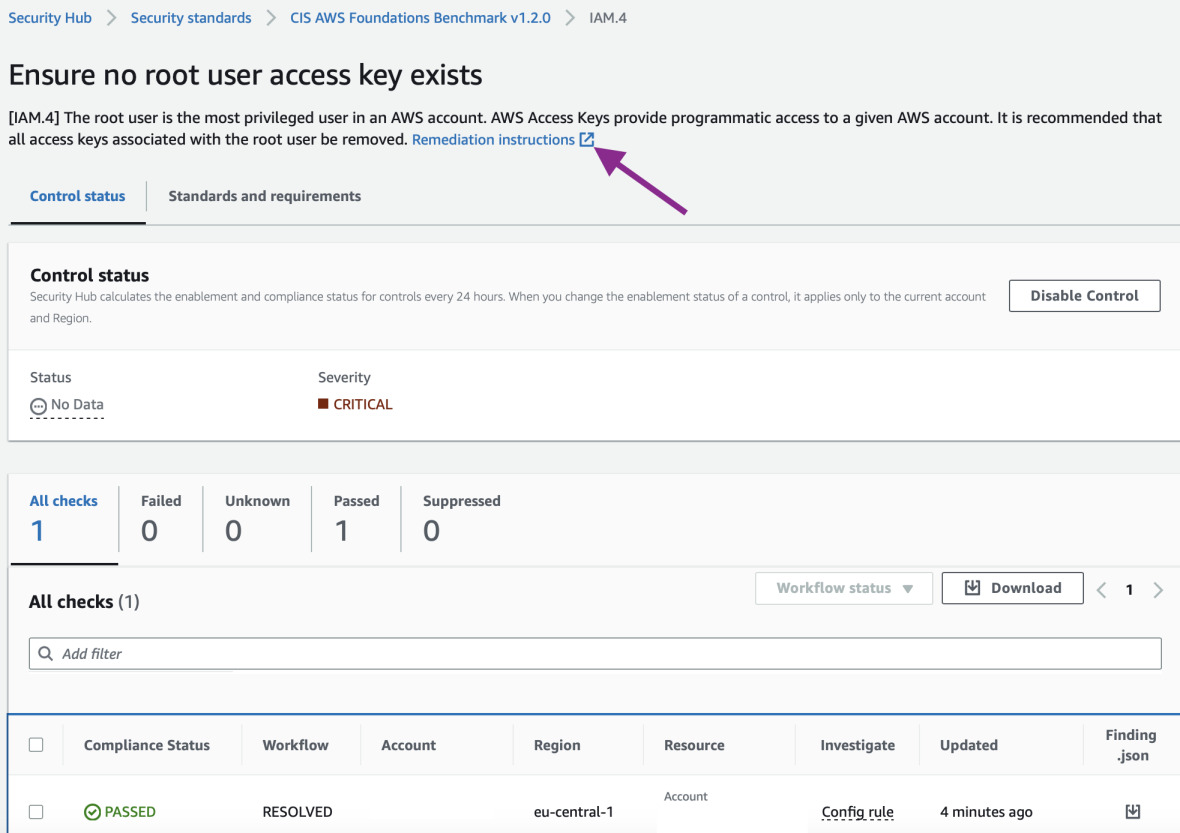
Inside the rule we can clearly see that the status is RESOLVED. So the
re-evaluation of the Config rule worked! In each of the controls in Security Hub
there's also a link in the description that will take you to AWS page with
instructions how to fix the issue.
To see the big picture, we have to wait around 24 hours or manually trigger and review the rules.
The following day
Now we clearly see our security score and we know what should be fixed. Some of the changes are trivial, for example password requirements for IAM users. Some are more tricky like disabling public access to your SQL database. If your application is configured to use such connection it would require rework and downtime to adapt to the new network configuration.
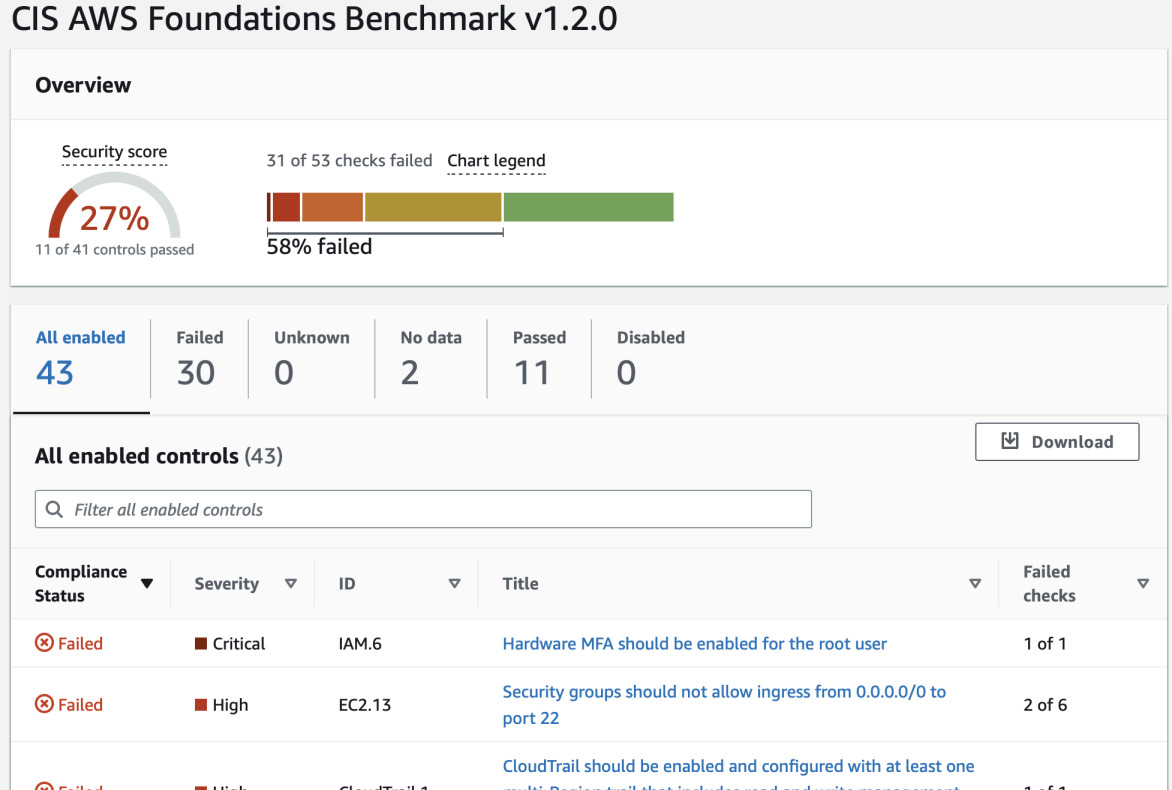
The selected security standard does not take into account all the best practices but it is a good start. We can go through the list of found issues and fix them one by one.
Fixing some of the found issues
We will go through some of the issues, particularly critical and high severity, and some others that are easy to fix.
Hardware MFA
The only critical problem that was found was existence of root access key (fixed in previous paragraph) and lack of hardware MFA for root user. For the latter it requires a device such as Yubikey or Passkey capable device (such as iPhone). Afterwards you have to remove all the virtual MFA methods (but before you do this, log out and try signing in again using the new security key).
SSH access
This one should be trivial to solve. Search for "what is my ip" in Google from
multiple places (home, office, etc.) or search for geo IP databases. Based on
the collected knowledge, add your subnets to the security group. For example if
your IP is 52.14.23.45, change this to 52.14.23.0/24 or 52.14.0.0/16. That
way you should not be locked out of SSH. But remember that you can always edit
the security group via console or CLI. However, the best approach would be to
use
AWS Client VPN
(OpenVPN compatible) or implement
port knocking.
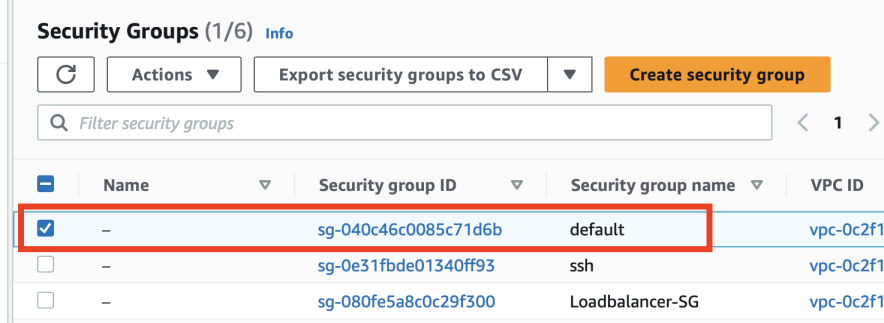
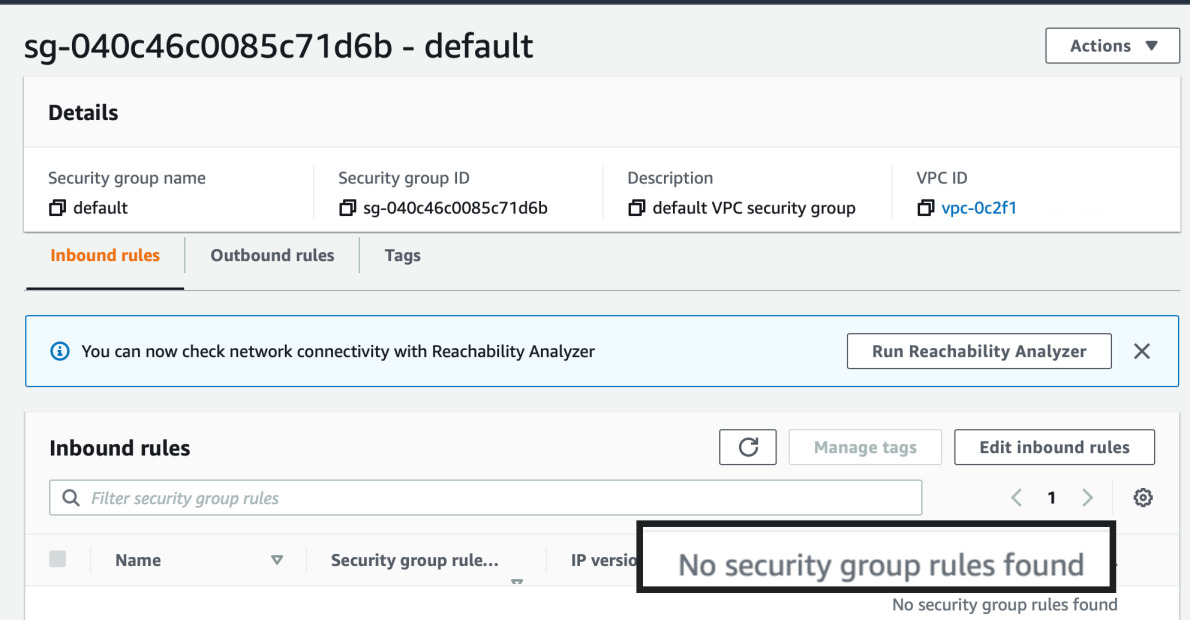
Default security group
Open your EC2 dashboard and click on Security Groups on the left. Look for
security group named default. Remove all inbound and outbound rules from it.
When starting a new EC2, RDS or anything that uses security groups, always pick
one that you created.
Multi-region CloudTrail
Go to CloudTrail and click Create trail. If this is first one, it will create
a multi-region trail with default settings.
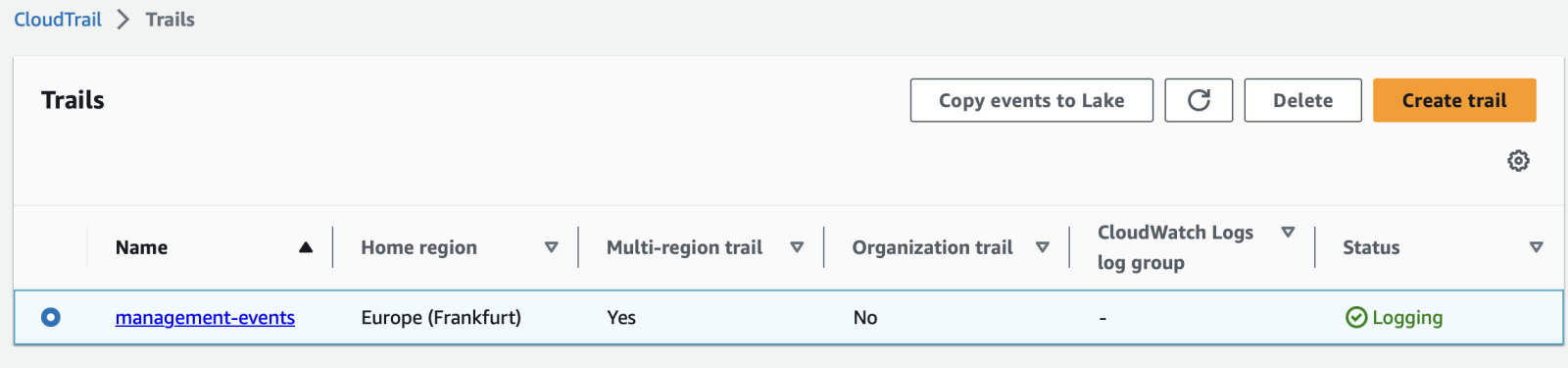
Next open it, click Edit, scroll down and enable Log file validation.
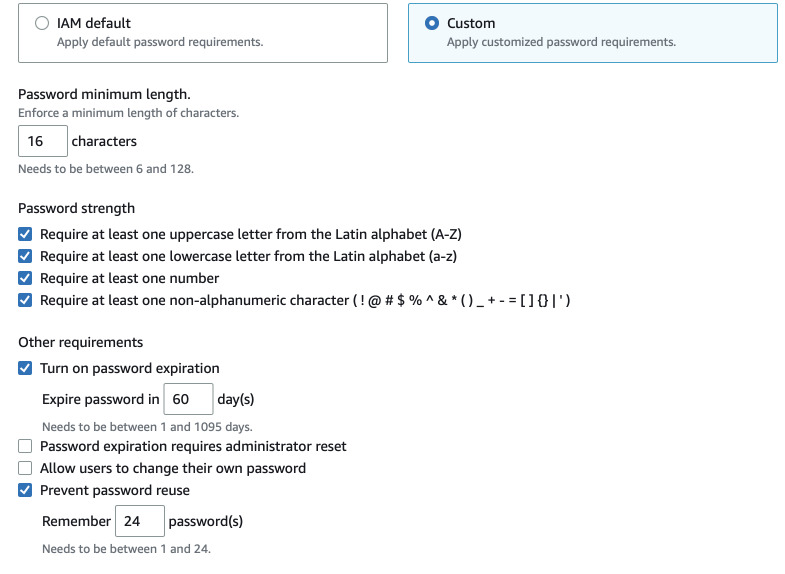
IAM password policies
This one is trivial. Go to IAM, click on Account settings on the left and edit
the password policy. Set minimum length to more than 14, select all the password
requirements, expire it every 90 days or less and remember last 24.
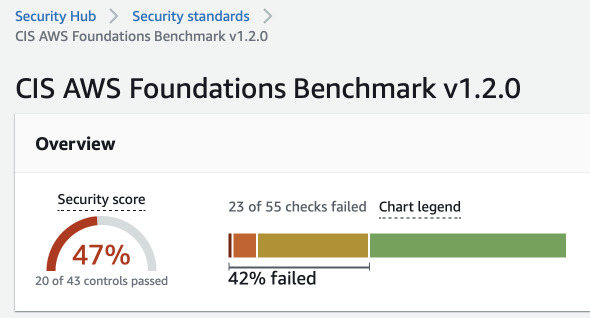
After another day, the score should go up. Here we see increase from 27% to 47%.
Going further
There are just examples of best practices. Once you complete or almost complete
Foundations 1.2, you can enable more standards such as
AWS Foundational Security Best Practices 1.0. But these are only about
security. You can also browse some other AWS best practices in Config. Open your
Config console, select Conformance packs and Deploy conformance pack. There
you can find both best security practices for individual services but also
operational practices.
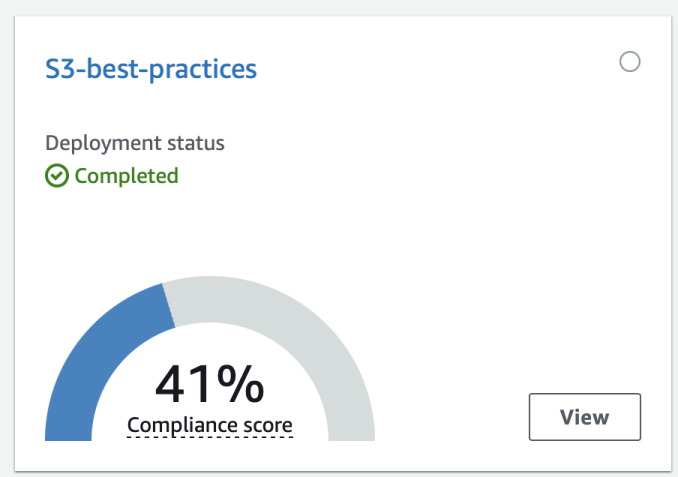
For example I deployed Operational best practices for S3. It also shows score on
how much practices you have implemented in your account. By clicking View you
can see exactly which rules are not compliant and what has to be changed.